Is Software and Hardware Solution That Acts as an Intermediary Between Two Systems.
An operating system acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and calculator hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs conveniently and efficiently.
An operating system is a software that manages computer hardware. The hardware must provide advisable mechanisms to ensure the correct operation of the computer arrangement and to foreclose user programs from interfering with the proper operation of the system.
Operating Organisation – Definition:
- An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of a estimator and the estimator hardware.
- A more than common definition is that the operating system is the one program running at all times on the computer (usually called the kernel), with all else being application programs.
- An operating organization is concerned with the allocation of resources and services, such every bit memory, processors, devices, and information. The operating organization correspondingly includes programs to manage these resources, such as a traffic controller, a scheduler, a memory management module, I/O programs, and a file system.
Functions of Operating arrangement – Operating system performs 3 functions:
- Convenience: An Bone makes a calculator more user-friendly to employ.
- Efficiency: An Bone allows the computer system resources to be used efficiently.
- Ability to Evolve: An Os should be constructed in such a way every bit to permit the effective development, testing, and introduction of new arrangement functions at the same time without interfering with service.
- Throughput: An Bone should exist constructed so that It can give maximum throughput(Number of tasks per unit of measurement fourth dimension).
Major Functionalities of Operating System:
- Resource Management: When parallel accessing happens in the OS means when multiple users are accessing the arrangement the OS works as Resources Manager, Its responsibility is to provide hardware to the user. It decreases the load in the organization.
- Procedure Management: It includes diverse tasks like scheduling, termination of the procedure. Bone manages diverse tasks at a time. Here CPU Scheduling happens means all the tasks would be washed by the many algorithms that apply for scheduling.
- Storage Direction: The file system machinery used for the management of the storage. NIFS, CFS, CIFS, NFS, etc. are some file systems. All the information stores in various tracks of Hard disks that all managed by the storage manager. It included Hard disk.
- Memory Management: Refers to the management of primary memory. The operating arrangement has to keep track, how much memory has been used and by whom. It has to determine which process needs retentivity space and how much. OS also has to allocate and deallocate the retentiveness space.
- Security/Privacy Management: Privacy is also provided by the Operating system past means of passwords so that unauthorized applications can't access programs or data. For example, Windows uses Kerberos hallmark to prevent unauthorized access to data.
The process operating system equally User Interface:
- User
- Organisation and application programs
- Operating system
- Hardware
Every general-purpose reckoner consists of the hardware, operating system, system programs, and awarding programs. The hardware consists of retention, CPU, ALU, and I/O devices, peripheral devices, and storage devices. System program consists of compilers, loaders, editors, Os, etc. The application program consists of business programs, database programs.
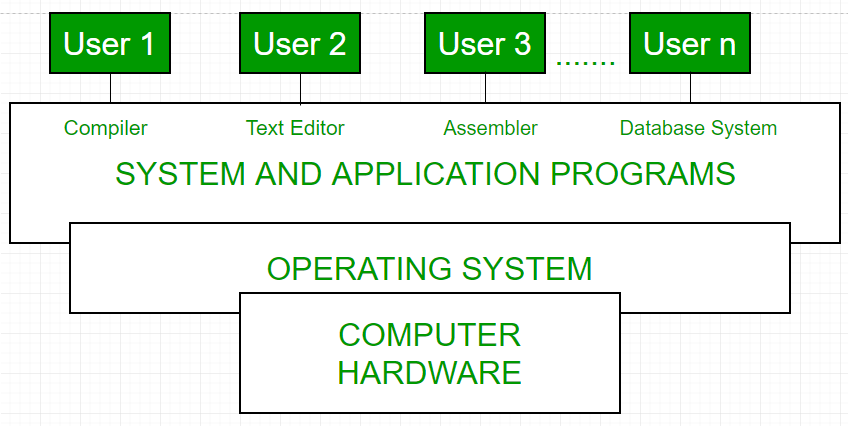
Fig1: Conceptual view of a computer system
Every computer must take an operating system to run other programs. The operating system coordinates the use of the hardware among the various organisation programs and awarding programs for diverse users. It merely provides an environment inside which other programs can do useful piece of work.
The operating system is a prepare of special programs that run on a estimator system that allows it to work properly. Information technology performs basic tasks such every bit recognizing input from the keyboard, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, sending output to the brandish screen, and decision-making peripheral devices.
Os is designed to serve two basic purposes:
- It controls the resource allotment and use of the computing System'southward resources among the diverse user and tasks.
- It provides an interface between the computer hardware and the programmer that simplifies and makes it feasible for coding, creation, debugging of awarding programs.
The Operating system must support the post-obit tasks. The tasks are:
- Provides the facilities to create, modification of programs and data files using an editor.
- Access to the compiler for translating the user program from loftier-level language to machine language.
- Provide a loader program to motion the compiled program code to the computer's retention for execution.
- Provide routines that handle the details of I/O programming.
I/O System Management –
The module that keeps runway of the status of devices is chosen the I/O traffic controller. Each I/O device has a device handler that resides in a separate process associated with that device.
The I/O subsystem consists of
- A memory Direction component that includes buffering caching and spooling.
- A general device commuter interface.
Drivers for specific hardware devices.
Assembler –
The input to an assembler is an assembly language programme. The output is an object plan plus information that enables the loader to prepare the object program for execution. At one time, the computer programmer had at his disposal a basic machine that interpreted, through hardware, certain fundamental instructions. He would program this computer by writing a series of ones and Zeros (Auto language), identify them into the memory of the machine.
Compiler –
The High-level languages- examples are FORTRAN, COBOL, ALGOL, and PL/I are processed by compilers and interpreters. A compiler is a program that accepts a source program in a "high-level language "and produces a corresponding object plan. An interpreter is a program that appears to execute a source plan as if it was machine language. The same proper noun (FORTRAN, COBOL, etc.) is ofttimes used to designate both a compiler and its associated language.
Loader –
A Loader is a routine that loads an object program and prepares it for execution. At that place are various loading schemes: absolute, relocating, and direct-linking. In general, the loader must load, relocate and link the object program. The loader is a plan that places programs into retentiveness and prepares them for execution. In a uncomplicated loading scheme, the assembler outputs the automobile language translation of a program on a secondary device and a loader places it in the core. The loader places into memory the machine linguistic communication version of the user'south program and transfers command to it. Since the loader plan is much smaller than the assembler, those make more core available to the user's program.
History of Operating system –
The operating system has been evolving through the years. The following tabular array shows the history of OS.
| Generation | Year | Electronic device used | Types of OS Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 1945-55 | Vacuum Tubes | Plug Boards |
| Second | 1955-65 | Transistors | Batch Systems |
| Third | 1965-lxxx | Integrated Circuits(IC) | Multiprogramming |
| Fourth | Since 1980 | Large Scale Integration | PC |
Types of Operating System –
- Batch Operating System- Sequence of jobs in a program on a computer without manual interventions.
- Time-sharing operating System- allows many users to share the computer resource. (Max utilization of the resources).
- Distributed operating Organization- Manages a group of unlike computers and makes appear to exist a single computer.
- Network operating arrangement- computers running in different operating systems can participate in a mutual network (It is used for security purposes).
- Real-time operating organisation – meant applications to set the deadlines.
Examples of Operating System are –
- Windows (GUI based, PC)
- GNU/Linux (Personal, Workstations, Internet service provider, File and print server, Three-tier client/Server)
- macOS (Macintosh), used for Apple tree'southward personal computers and workstations (MacBook, iMac).
- Android (Google's Operating Arrangement for smartphones/tablets/smartwatches)
- iOS (Apple tree'southward Os for iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch)
References –
Operating Organization Concepts – Volume
Introduction to Operating System – NPTEL
0 Response to "Is Software and Hardware Solution That Acts as an Intermediary Between Two Systems."
Post a Comment